Building a Black Hole Shader in Godot 4
My upcoming hobby 4X game takes place over an entire galaxy, and what's at the center of every galaxy? A supermassive black hole. So, we need to make one.
This isn't a physically accurate simulation. We're building a stylized effect that looks right, using simplified physics approximations. The real math behind Gargantua involved over a year of work by Kip Thorne and the DNEG VFX team. Ours will take about 400 lines of shader code.
Stage 1: Sphere Intersection
Every raymarch shader needs to know where the ray enters and exits the volume. We use standard ray-sphere intersection math:
vec2 intersect_sphere(vec3 ray_origin, vec3 ray_dir, vec3 sphere_centre, float radius) {
vec3 offset = ray_origin - sphere_centre;
float b = 2.0 * dot(offset, ray_dir);
float c = dot(offset, offset) - radius * radius;
float discriminant = b * b - 4.0 * c;
if (discriminant > 0.0) {
float s = sqrt(discriminant);
float dst_near = max(0.0, (-b - s) * 0.5);
float dst_far = (-b + s) * 0.5;
if (dst_far >= 0.0) {
return vec2(dst_near, dst_far - dst_near);
}
}
return vec2(MAX_FLOAT, 0.0);
}
This returns two values: the distance to where the ray enters the sphere, and how far it travels through it. If the ray misses entirely, we return a sentinel value.

The vertex shader is minimal - we just extract the world position and object scale for use in the fragment shader:
void vertex() {
frag_pos_ws = (MODEL_MATRIX * vec4(VERTEX, 1.0)).xyz;
centre = MODEL_MATRIX[3].xyz;
object_scale = vec3(
length(MODEL_MATRIX[0].xyz),
length(MODEL_MATRIX[1].xyz),
length(MODEL_MATRIX[2].xyz)
);
}
Stage 2: Raymarching Foundation
With sphere intersection working, we can step through it. The basic loop looks like this:
vec3 current_ray_pos = ray_origin + ray_dir * sphere_entry_distance;
vec3 current_ray_dir = ray_dir;
for (int i = 0; i < ray_steps; i++) {
// Do something at each step
current_ray_pos += current_ray_dir * step_size;
// Exit if we've left the sphere
if (length(current_ray_pos - centre) > sphere_radius) {
break;
}
}
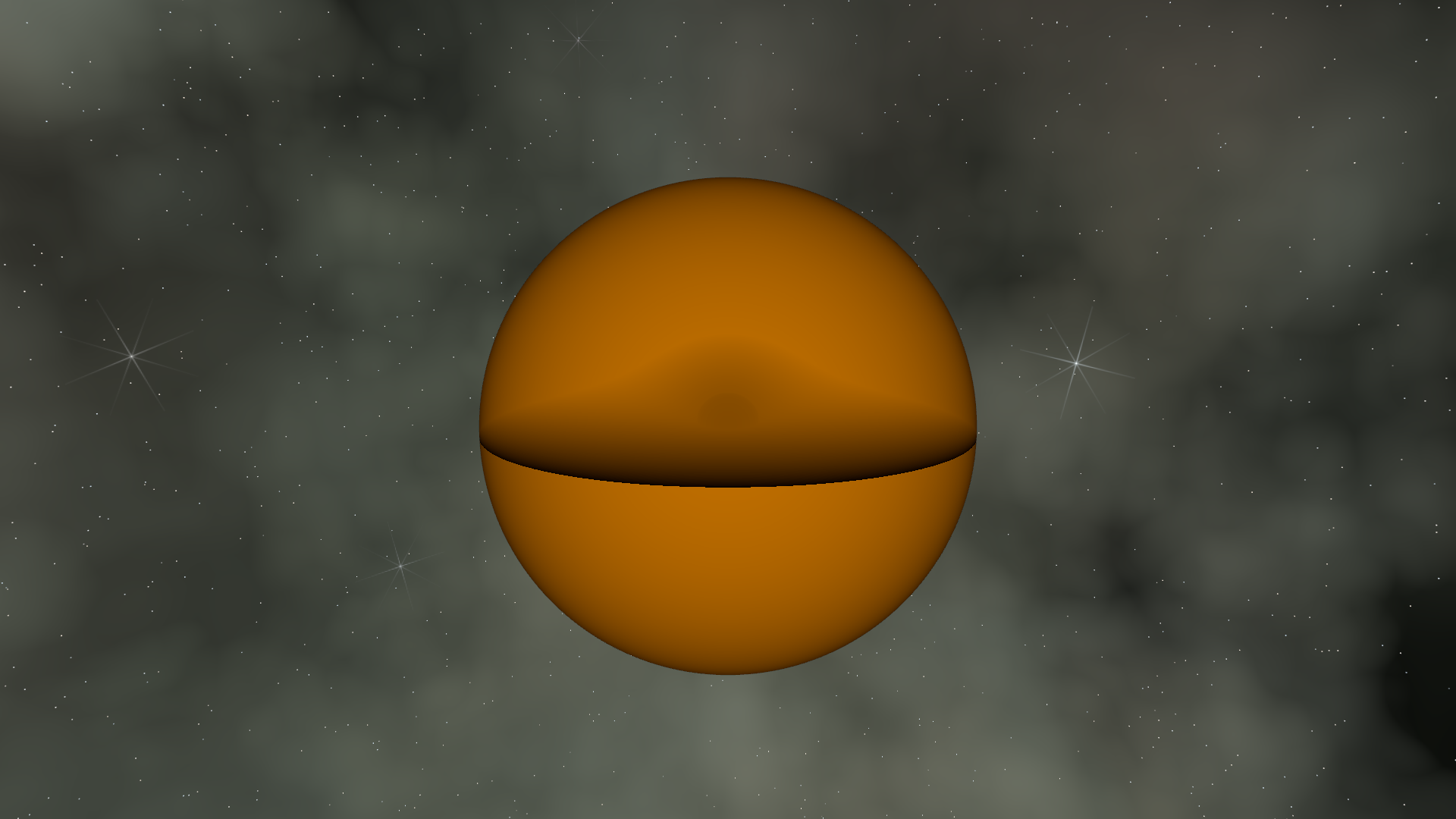

The heatmap shows how many steps each pixel required. More steps near the edges
where the ray travels further through the sphere. This is why ray_steps is a
key performance knob - too few and you get banding artifacts, too many and your
GPU melts.
Stage 3: Gravitational Lensing
Here's where the magic happens. At each step, we bend the ray toward the center using an inverse-square force (mimicking gravity):
vec3 dir_to_centre = centre - current_ray_pos;
float dst_to_centre = length(dir_to_centre);
dir_to_centre /= dst_to_centre; // Normalize
float norm_dst = max(dst_to_centre / sphere_radius, 1e-4);
float force = g_const / (norm_dst * norm_dst); // Inverse-square
current_ray_dir = normalize(current_ray_dir + dir_to_centre * force * step_size);
The g_const uniform controls how strongly gravity bends light. Higher values
create more extreme lensing. The force follows an inverse-square law (1/r²),
increasing rapidly as you approach the center - just like real gravity.
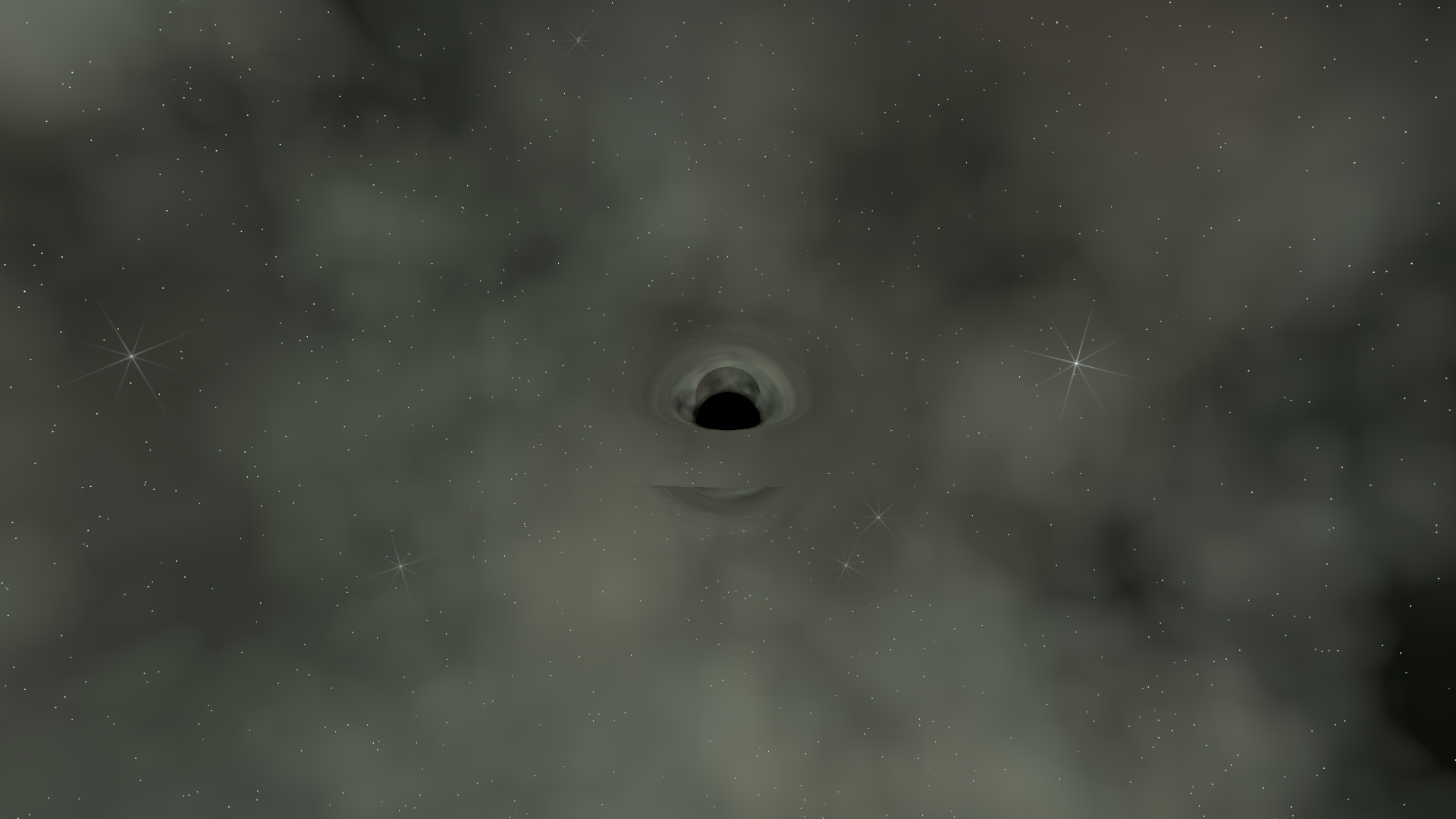

Notice how the stars warp around the center. Light rays passing close to the black hole bend dramatically, while distant rays barely deflect. With perfect alignment, this creates an Einstein ring - but any viewing angle shows gravitational lensing.
Stage 4: The Event Horizon
At some radius, the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing escapes. We model this as simple absorption:
if (dst_to_centre <= event_horizon_radius) {
black_hole_mask = 1.0;
break;
}
To avoid hard aliased edges, we add a soft falloff zone around the horizon:
float falloff_zone = event_horizon_radius * 1.5;
if (curr_dst_to_centre < falloff_zone) {
float proximity = 1.0 - (curr_dst_to_centre - event_horizon_radius)
/ (falloff_zone - event_horizon_radius);
black_hole_mask = max(black_hole_mask, clamp(proximity, 0.0, 1.0));
}
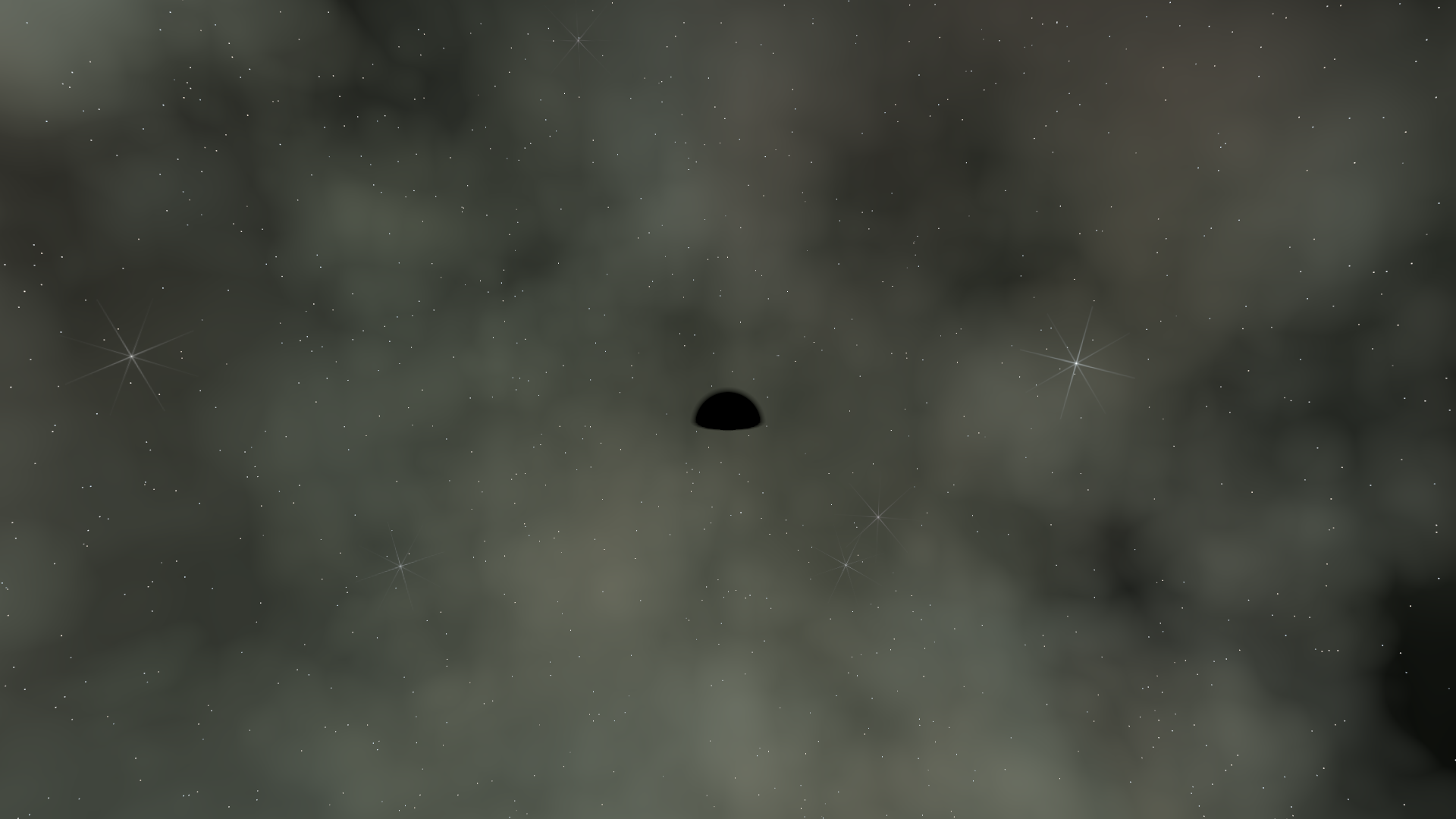

The black_hole_mask accumulates as rays get close to the horizon, creating a
smooth transition into darkness rather than a sharp circle.
Stage 5: Detecting the Disc
The accretion disc is modeled as an infinitely thin plane perpendicular to the black hole's up vector. We detect when a ray crosses this plane by checking for a sign change:
float prev_plane_dist = dot(prev_ray_pos - centre, disc_dir);
float curr_plane_dist = dot(current_ray_pos - centre, disc_dir);
if (prev_plane_dist * curr_plane_dist < 0.0) {
// Ray crossed the disc plane this step
float interp = abs(prev_plane_dist) / (abs(prev_plane_dist) + abs(curr_plane_dist));
vec3 crossing_pos = mix(prev_ray_pos, current_ray_pos, interp);
}
The linear interpolation finds the exact crossing point between our two sample positions. This is more accurate than just using the current position, especially with larger step sizes.
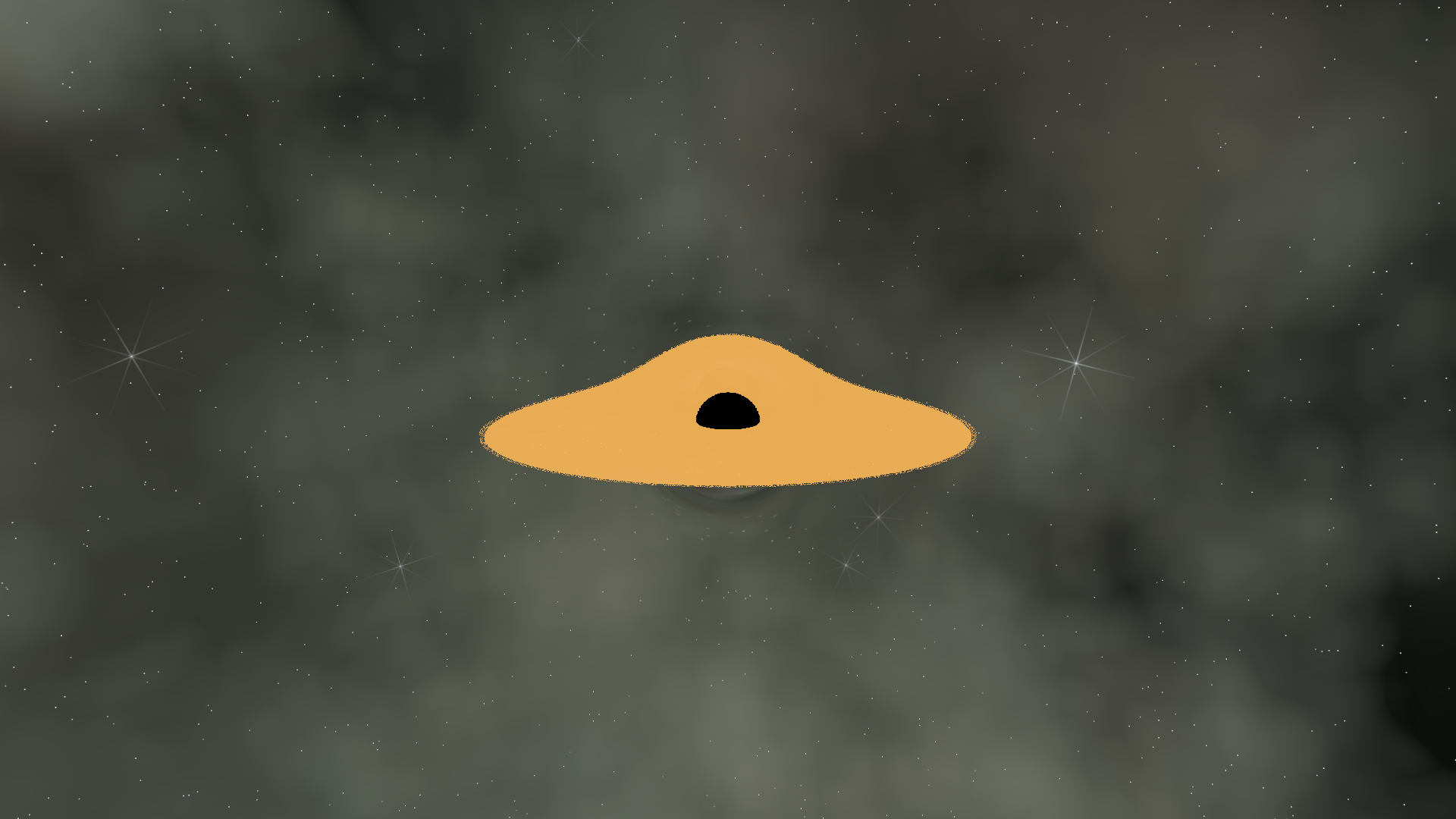

We also check that the crossing point falls within the disc's inner and outer radii. The inner edge exists because matter too close to the horizon falls in rather than orbiting.
Stage 6: Disc Temperature Gradient
Real accretion discs are hotter near the center where matter is compressed and moving faster. We model this with a radial color gradient:
vec2 disc_uv(vec3 planar_disc_pos, float radius) {
float sample_dist = length(planar_disc_pos) / max(radius, 1e-6);
float phi = atan(planar_disc_pos.z, planar_disc_pos.x);
phi = phi / (2.0 * PI) + 0.5;
return vec2(sample_dist, phi);
}
The UV coordinates give us radial distance (u) and angular position (v). We use the radial coordinate to blend between a hot inner color (white-yellow) and a cooler outer color:
vec3 inner_color = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 0.95);
float radial_t = clamp(uv.x, 0.0, 1.0);
vec3 temp_color = mix(inner_color, base_color, pow(radial_t, 0.6));
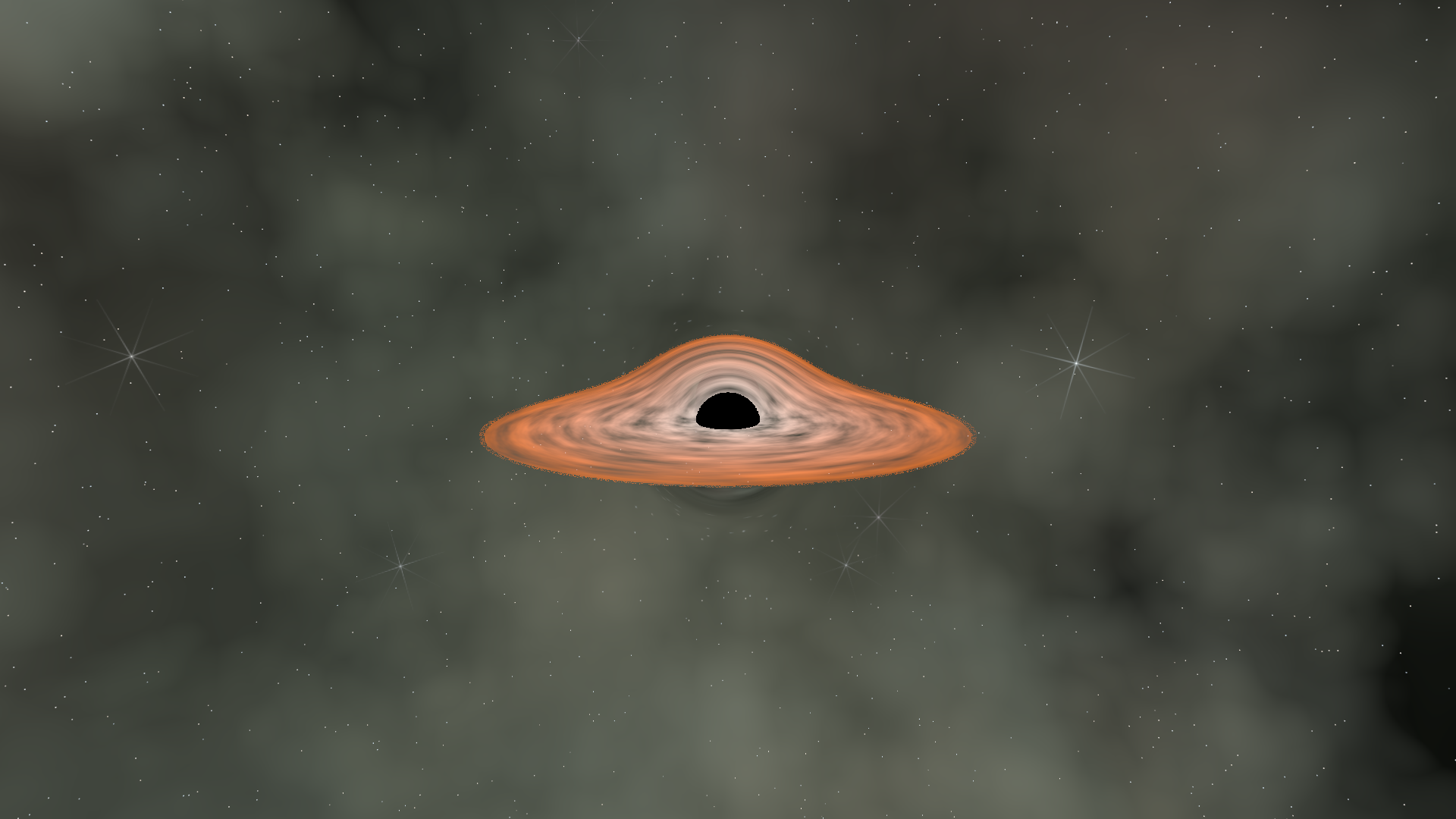
The pow(radial_t, 0.6) gives us a non-linear falloff - the hot inner region
stays bright longer before transitioning to the outer color.
Stage 7: Doppler Beaming
When matter orbits at relativistic speeds, the side moving toward you appears brighter than the side moving away. This is called Doppler beaming, and it's why real black hole images show asymmetric brightness.
We simulate this by comparing distances after a small rotation:
vec3 rotated_pos = rotate_about_axis(planar_disc_pos, disc_dir, 0.01);
float doppler_dist = (length(rotated_pos - camera_pos) - length(planar_disc_pos - camera_pos))
/ safe_radius;
float doppler_contribution = doppler_dist * disc_speed * doppler_beaming_factor;

The approaching side gets significantly brighter. Combined with the temperature gradient, this creates the distinctive asymmetric look of accretion discs.
Stage 8: Procedural Turbulence
A perfectly smooth disc looks artificial. Real accretion discs have turbulent flow patterns. We generate these procedurally using Fractional Brownian Motion (FBM) - layered noise at different frequencies:
float seamless_fbm_cylinder(float u, float v, float scale, float time, int octaves) {
// Convert angular coordinate to circle to avoid seams
float angle = v * 2.0 * PI;
vec3 cyl_pos = vec3(u * scale, cos(angle) * scale * 0.5, sin(angle) * scale * 0.5);
cyl_pos.x += time; // Animate
float value = 0.0;
float amplitude = 0.5;
float frequency = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < octaves; i++) {
float n1 = noise2d(cyl_pos.xy * frequency);
float n2 = noise2d(cyl_pos.xz * frequency + 100.0);
value += amplitude * mix(n1, n2, 0.5);
amplitude *= 0.5;
frequency *= 2.0;
}
return value;
}
The trick here is using cylindrical coordinates. If we just used 2D noise with the angular coordinate directly, we'd get a visible seam where 0 meets 2π. By wrapping the angle onto a circle in 3D space, the noise tiles seamlessly.
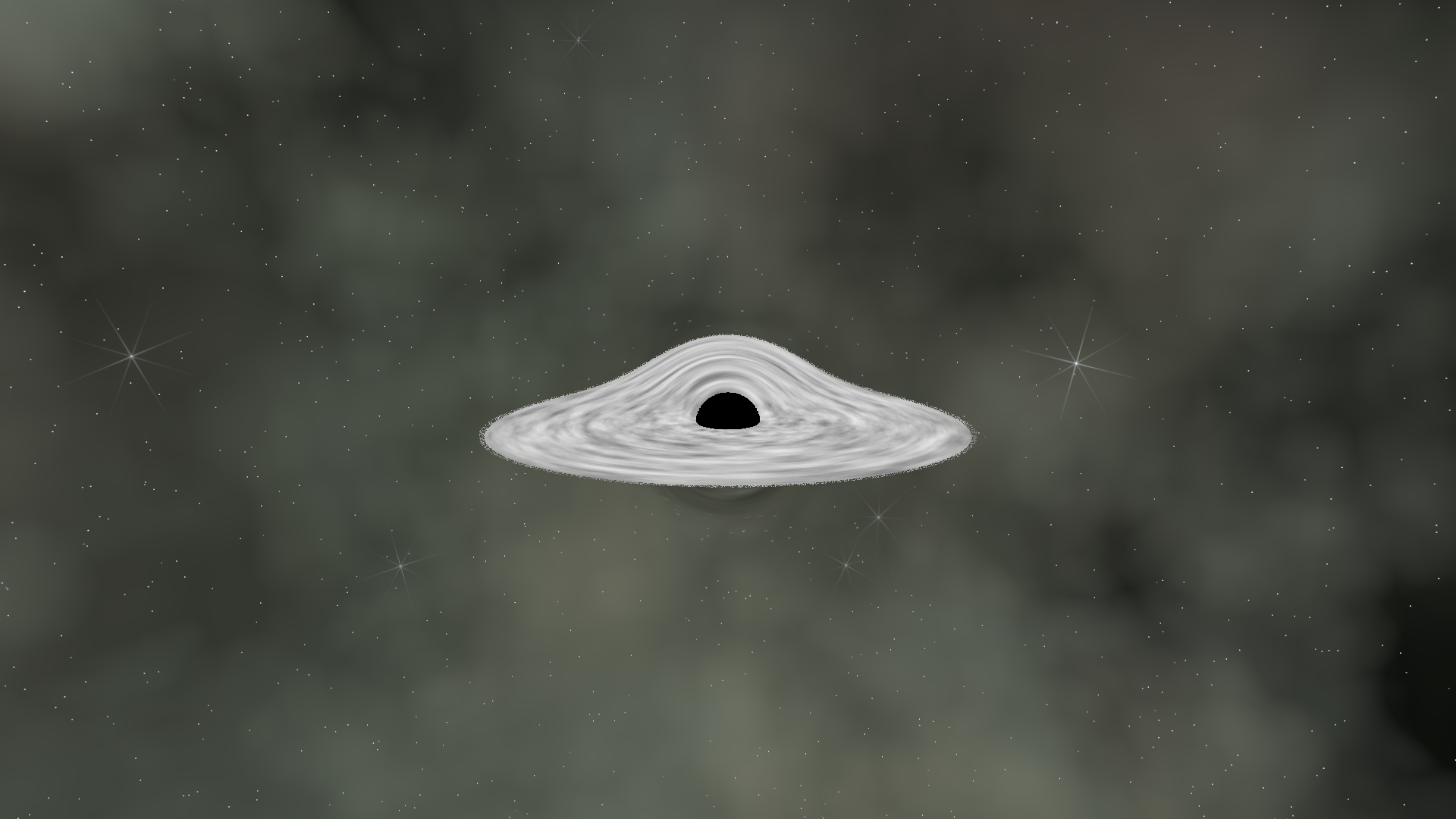
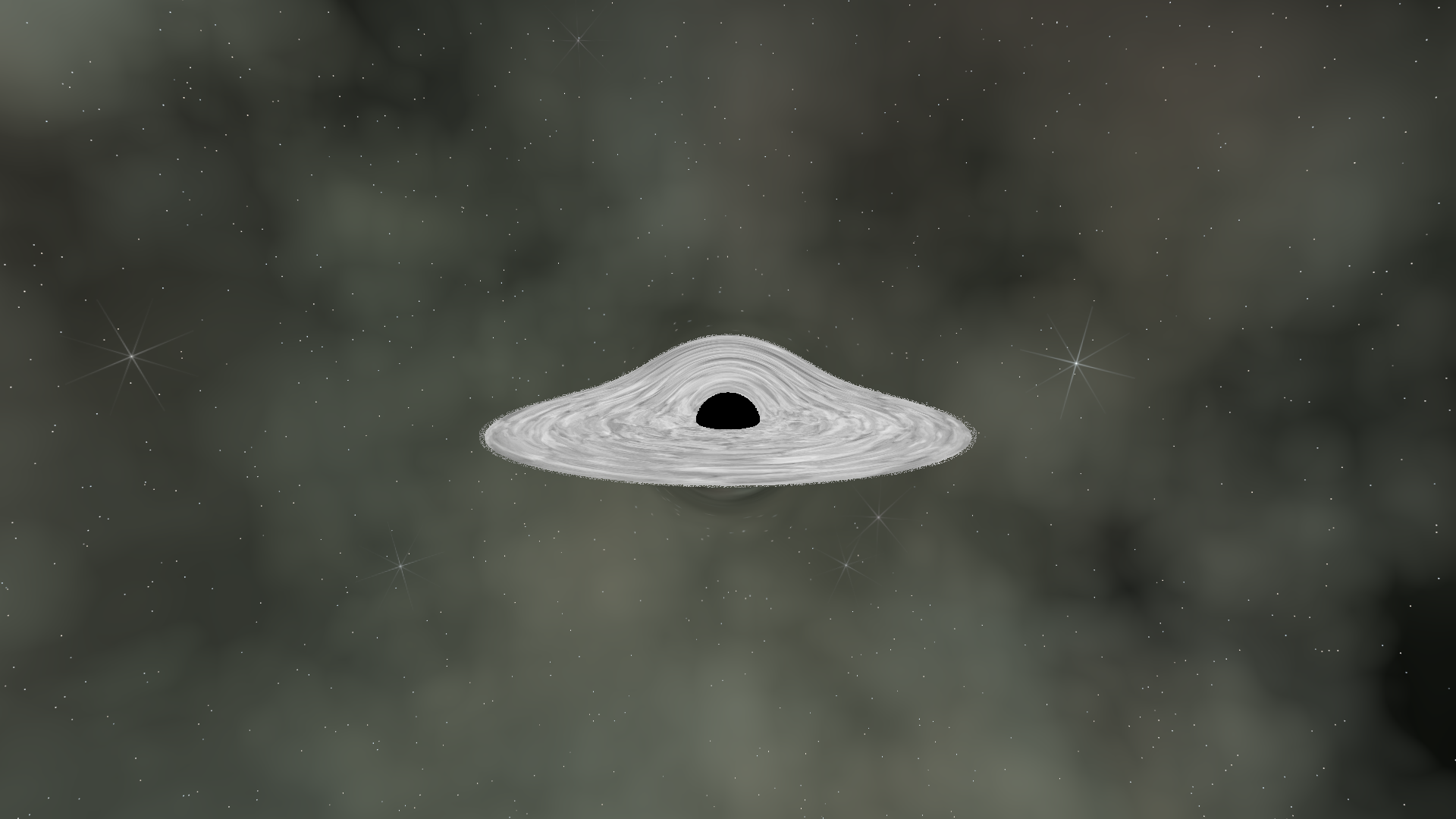


The second image shows turbulent displacement applied - we use one layer of FBM to distort the coordinates of another, creating swirling patterns.
Stage 9: Angular Streaks
For extra visual interest, we add radial streaks that spiral around the disc:
float soft_edge(float radius_norm, float angle, float time) {
float scaled_angle = angle * streak_count;
float edge_noise = seamless_noise1d(scaled_angle + time * 0.1, streak_count * period);
float falloff = 1.0 - smoothstep(falloff_start, 1.0, radius_norm);
return falloff;
}
These create the appearance of density variations in the orbiting material.
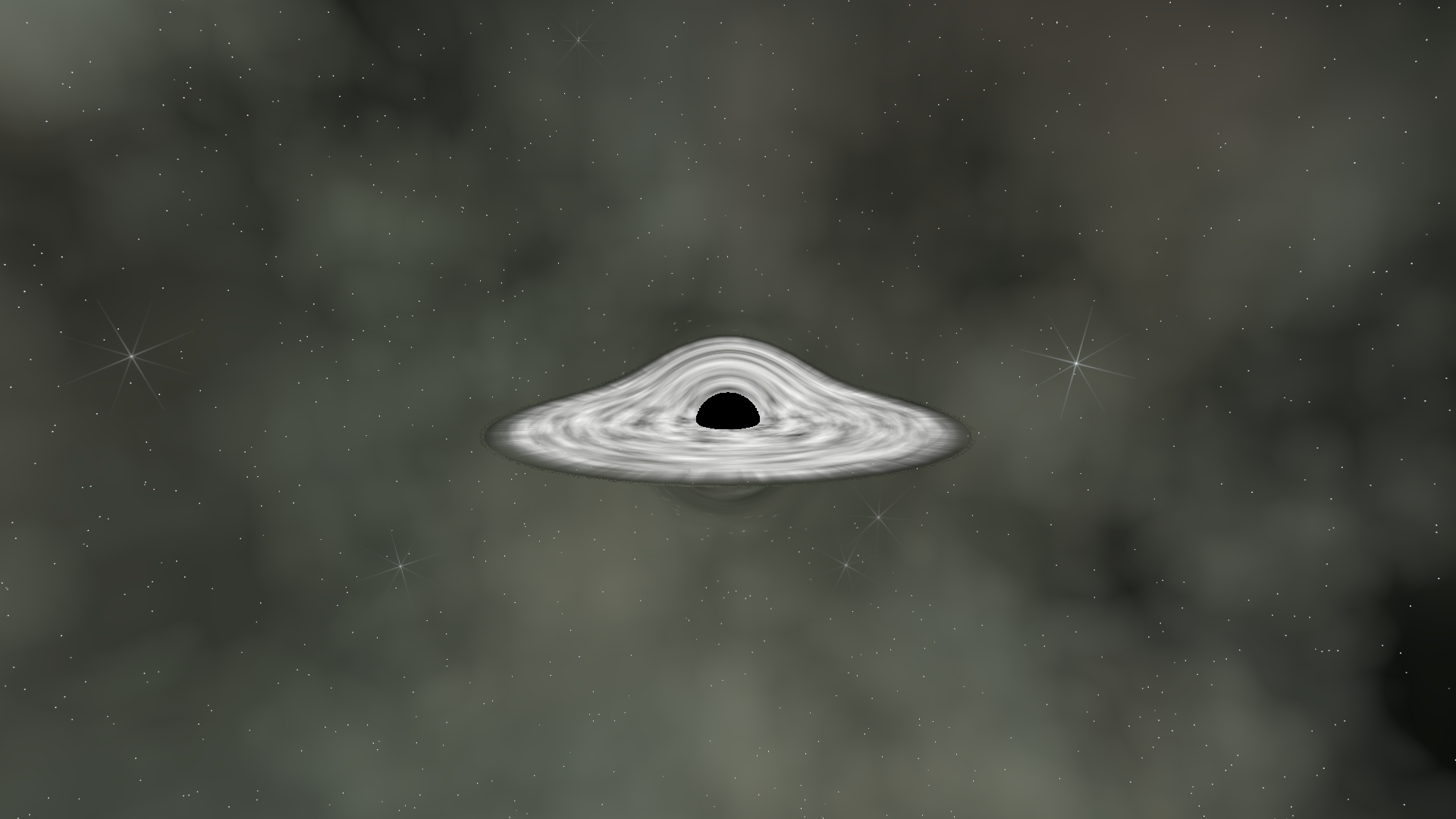

Stage 10: Screen-Space Lensing
After raymarching, we have a bent ray direction. We project this back to screen space to find where to sample the background:
vec3 distorted_ray_dir = has_sphere ? current_ray_dir : ray_dir;
vec4 ray_camera_space = VIEW_MATRIX * vec4(distorted_ray_dir, 0.0);
vec4 ray_uv_projection = PROJECTION_MATRIX * vec4(ray_camera_space.xyz, 0.0);
vec2 distorted_screen_uv = ray_uv_projection.xy * 0.5 + 0.5;
We blend based on how much the ray actually bent, creating smooth transitions at the sphere boundary:
float ray_bend = 1.0 - dot(ray_dir, current_ray_dir);
float bend_blend = smoothstep(0.0, 0.15, ray_bend);
distorted_screen_uv = mix(screen_uv, distorted_screen_uv, bend_blend);
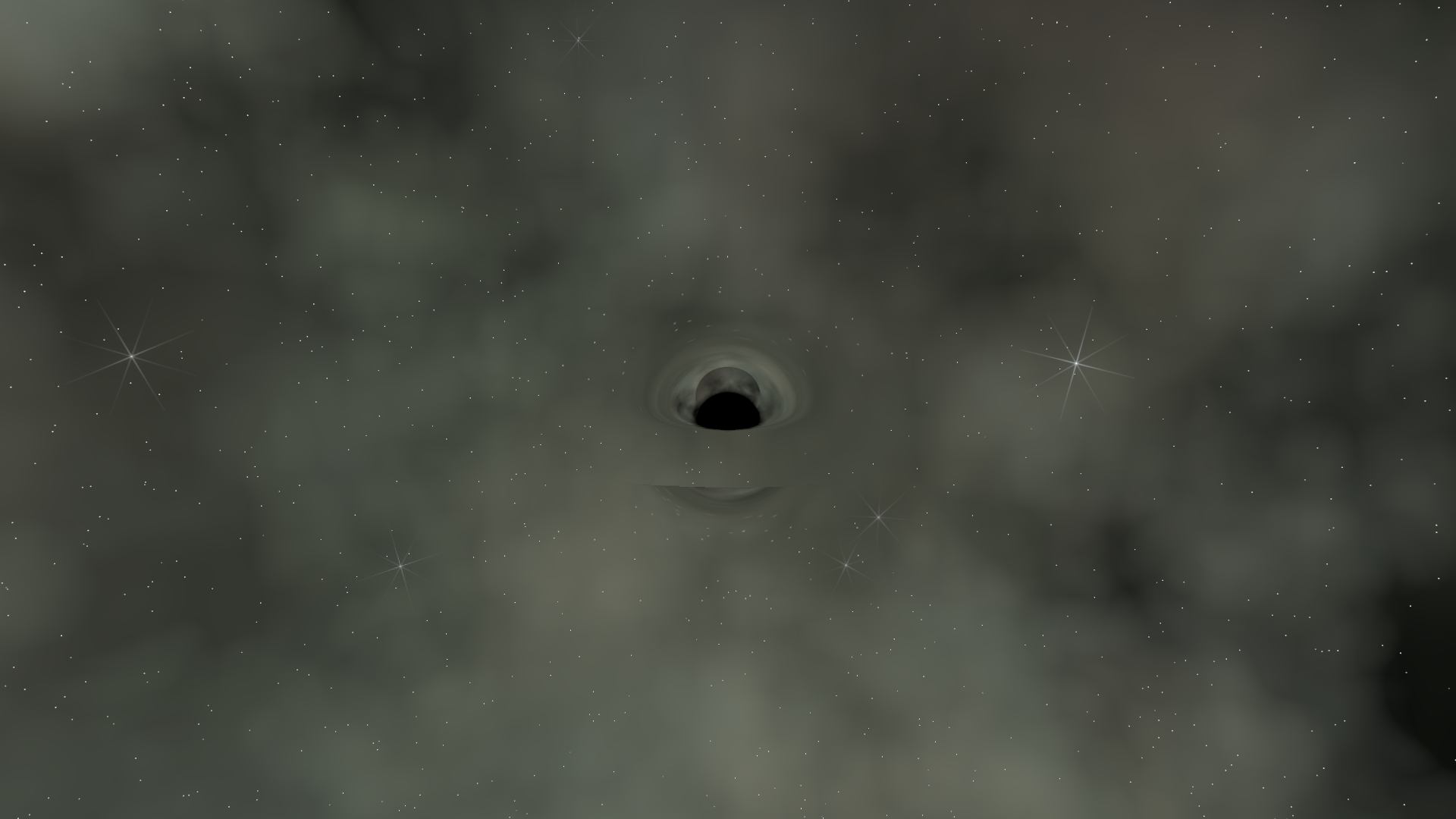

This is the full gravitational lensing effect - the background warps dramatically near the event horizon.
Putting It Together
The final composition blends the lensed background with the disc emission:
vec3 background_col = texture(screen_texture, distorted_screen_uv).rgb * (1.0 - black_hole_mask);
vec3 final_disc_col = calc_disc_color(...);
disc_hit *= tex_col * disc_color.a * streaks * horizon_fade * radial_falloff;
vec3 col = mix(background_col, final_disc_col, disc_hit);
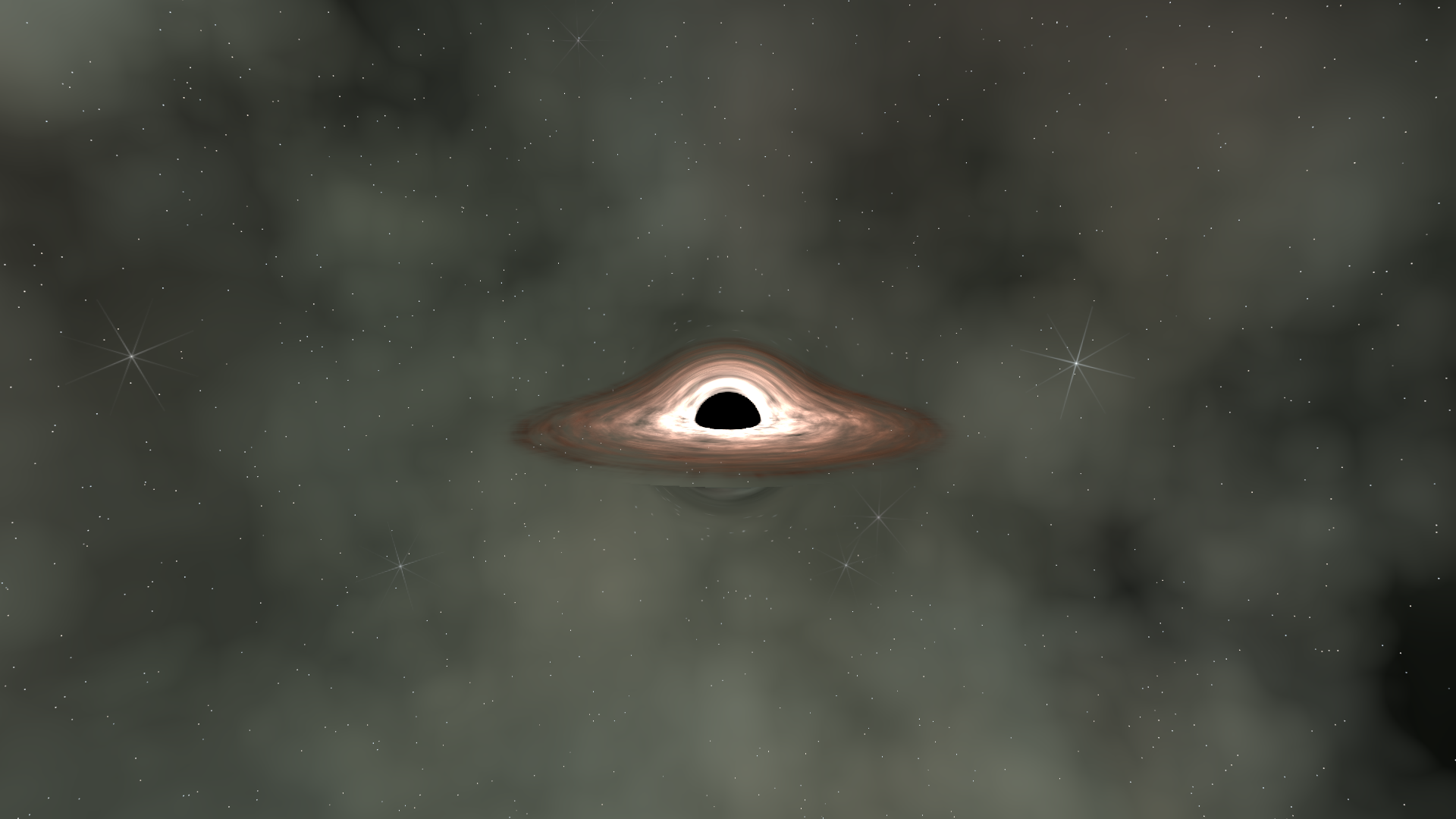

Full Shader
/*
Copyright 2026 Tyler Kennedy
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of
this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in
the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies
of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do
so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
Procedural Black Hole Shader
============================
Mental model:
- Raymarch inside a bounding sphere, bending the ray toward the center.
- If the ray hits the event horizon, it is absorbed; if it hits the disc, it emits.
- The final ray direction warps the screen sample to create lensing.
This is a stylized effect with simple physics approximations.
*/
shader_type spatial;
render_mode unshaded, cull_disabled, depth_draw_never;
uniform sampler2D disc_texture : filter_linear, repeat_enable;
uniform float disc_outer_radius : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 1.0;
uniform float disc_inner_radius : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 0.25;
uniform float disc_speed : hint_range(0.0, 10.0) = 2.0;
uniform vec4 disc_color : source_color = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
uniform float doppler_beaming_factor : hint_range(0.0, 200.0) = 66.0;
uniform float hue_radius : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 0.75;
uniform float hue_shift_factor : hint_range(-1.0, 1.0) = -0.03;
uniform float streak_intensity : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 0.5;
uniform float streak_count : hint_range(1.0, 50.0) = 20.0;
uniform float turbulence_intensity : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 0.3;
uniform float turbulence_scale : hint_range(0.5, 10.0) = 3.0;
uniform float turbulence_speed : hint_range(0.0, 2.0) = 0.5;
uniform int turbulence_octaves : hint_range(1, 6) = 4;
uniform int ray_steps : hint_range(32, 512) = 256;
uniform float step_size : hint_range(0.001, 1.0) = 0.1;
uniform float ss_radius : hint_range(0.0, 1.0) = 0.1;
uniform float g_const : hint_range(0.0, 2.0) = 0.3;
uniform sampler2D screen_texture : hint_screen_texture, filter_linear_mipmap;
const float MAX_FLOAT = 3.402823466e+38;
const float SEAM_BLEND_START = 0.9;
varying vec3 frag_pos_ws;
varying vec3 centre;
varying vec3 object_scale;
void vertex() {
frag_pos_ws = (MODEL_MATRIX * vec4(VERTEX, 1.0)).xyz;
centre = MODEL_MATRIX[3].xyz;
object_scale = vec3(
length(MODEL_MATRIX[0].xyz),
length(MODEL_MATRIX[1].xyz),
length(MODEL_MATRIX[2].xyz)
);
}
float hash(float n) { return fract(sin(n) * 43758.5453); }
float noise1d(float x) {
float i = floor(x);
float f = fract(x);
f = f * f * (3.0 - 2.0 * f);
return mix(hash(i), hash(i + 1.0), f);
}
float noise2d(vec2 p) {
vec2 i = floor(p);
vec2 f = fract(p);
f = f * f * (3.0 - 2.0 * f);
float a = hash(dot(i, vec2(1.0, 157.0)));
float b = hash(dot(i + vec2(1.0, 0.0), vec2(1.0, 157.0)));
float c = hash(dot(i + vec2(0.0, 1.0), vec2(1.0, 157.0)));
float d = hash(dot(i + vec2(1.0, 1.0), vec2(1.0, 157.0)));
return mix(mix(a, b, f.x), mix(c, d, f.x), f.y);
}
float seamless_fbm_cylinder(float u, float v, float scale, float time, int octaves) {
float angle = v * 2.0 * PI;
vec3 cyl_pos = vec3(u * scale, cos(angle) * scale * 0.5, sin(angle) * scale * 0.5);
cyl_pos.x += time;
float value = 0.0;
float amplitude = 0.5;
float frequency = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < octaves; i++) {
float n1 = noise2d(cyl_pos.xy * frequency);
float n2 = noise2d(cyl_pos.xz * frequency + 100.0);
value += amplitude * mix(n1, n2, 0.5);
amplitude *= 0.5;
frequency *= 2.0;
}
return value;
}
vec2 turbulent_displacement_seamless(float u, float v, float time, float scale, float intensity, int octaves) {
vec2 offset = vec2(
seamless_fbm_cylinder(u, v, scale, time * 0.7, octaves),
seamless_fbm_cylinder(u, v + 0.37, scale, time * 0.5, octaves)
);
return (offset - 0.5) * intensity;
}
float seamless_noise1d(float x, float period) {
float t = fract(x / period);
float n1 = noise1d(x);
float n2 = noise1d(x - period);
return mix(n1, n2, smoothstep(SEAM_BLEND_START, 1.0, t));
}
float soft_edge(float radius_norm, float angle, float time) {
float period = 2.0 * PI;
float scaled_angle1 = angle * streak_count;
float scaled_angle2 = angle * streak_count * 2.3 + 100.0;
float edge_noise = seamless_noise1d(scaled_angle1 + time * 0.1, streak_count * period) * 0.5 + 0.5;
float edge_noise2 = seamless_noise1d(scaled_angle2 + time * 0.15, streak_count * 2.3 * period) * 0.5 + 0.5;
float combined_noise = edge_noise * 0.6 + edge_noise2 * 0.4;
float falloff_start = 0.6 + combined_noise * streak_intensity * 0.4;
float falloff = 1.0 - smoothstep(falloff_start, 1.0, radius_norm);
return falloff;
}
vec2 intersect_sphere(vec3 ray_origin, vec3 ray_dir, vec3 sphere_centre, float radius) {
vec3 offset = ray_origin - sphere_centre;
float b = 2.0 * dot(offset, ray_dir);
float c = dot(offset, offset) - radius * radius;
float discriminant = b * b - 4.0 * c;
if (discriminant > 0.0) {
float s = sqrt(discriminant);
float dst_near = max(0.0, (-b - s) * 0.5);
float dst_far = (-b + s) * 0.5;
if (dst_far >= 0.0) {
return vec2(dst_near, dst_far - dst_near);
}
}
return vec2(MAX_FLOAT, 0.0);
}
float remap(float v, float min_old, float max_old, float min_new, float max_new) {
float denom = max_old - min_old;
if (abs(denom) < 1e-6) {
return min_new;
}
return min_new + (v - min_old) * (max_new - min_new) / denom;
}
vec2 disc_safe_radii() {
float safe_outer = max(disc_outer_radius, 1e-4);
float safe_inner = clamp(disc_inner_radius, 0.0, safe_outer - 1e-4);
return vec2(safe_inner, safe_outer);
}
vec2 disc_uv(vec3 planar_disc_pos, float radius) {
float sample_dist = length(planar_disc_pos) / max(radius, 1e-6);
float phi = atan(planar_disc_pos.z, planar_disc_pos.x);
phi = phi / (2.0 * PI) + 0.5;
return vec2(sample_dist, phi);
}
vec3 linear_to_gamma(vec3 col) {
col = max(col, vec3(0.0));
return max(1.055 * pow(col, vec3(0.416666667)) - 0.055, vec3(0.0));
}
vec3 gamma_to_linear(vec3 col) {
return col * (col * (col * 0.305306011 + 0.682171111) + 0.012522878);
}
vec3 hdr_intensity(vec3 col, float intensity) {
col = linear_to_gamma(col);
col *= pow(2.0, intensity);
col = gamma_to_linear(col);
return col;
}
vec3 rgb_to_hsv(vec3 c) {
vec4 K = vec4(0.0, -1.0 / 3.0, 2.0 / 3.0, -1.0);
vec4 p = mix(vec4(c.bg, K.wz), vec4(c.gb, K.xy), step(c.b, c.g));
vec4 q = mix(vec4(p.xyw, c.r), vec4(c.r, p.yzx), step(p.x, c.r));
float d = q.x - min(q.w, q.y);
float e = 1.0e-10;
return vec3(abs(q.z + (q.w - q.y) / (6.0 * d + e)), d / (q.x + e), q.x);
}
vec3 hsv_to_rgb(vec3 c) {
vec4 K = vec4(1.0, 2.0 / 3.0, 1.0 / 3.0, 3.0);
vec3 p = abs(fract(c.xxx + K.xyz) * 6.0 - K.www);
return c.z * mix(K.xxx, clamp(p - K.xxx, 0.0, 1.0), c.y);
}
vec3 rotate_about_axis(vec3 v, vec3 axis, float rotation) {
float s = sin(rotation);
float c = cos(rotation);
float omc = 1.0 - c;
axis = normalize(axis);
mat3 rot = mat3(
vec3(omc * axis.x * axis.x + c, omc * axis.x * axis.y + axis.z * s, omc * axis.z * axis.x - axis.y * s),
vec3(omc * axis.x * axis.y - axis.z * s, omc * axis.y * axis.y + c, omc * axis.y * axis.z + axis.x * s),
vec3(omc * axis.z * axis.x + axis.y * s, omc * axis.y * axis.z - axis.x * s, omc * axis.z * axis.z + c)
);
return rot * v;
}
vec3 calc_disc_color(vec3 base_color, vec3 planar_disc_pos, vec3 disc_dir, vec3 camera_pos, float u, float v, float radius, float time) {
float radial_t = clamp(u, 0.0, 1.0);
float turb_time = time * turbulence_speed;
float turb_noise = seamless_fbm_cylinder(u * 2.0, v, turbulence_scale, turb_time, turbulence_octaves);
vec2 swirl_offset = turbulent_displacement_seamless(u * 2.0, v, turb_time, turbulence_scale * 0.5, turbulence_intensity * 0.3, turbulence_octaves);
float swirl_noise = seamless_fbm_cylinder(u * 2.0 + swirl_offset.x, v + swirl_offset.y, turbulence_scale * 1.5, turb_time * 0.5, turbulence_octaves);
float combined_turb = mix(turb_noise, swirl_noise, 0.5);
float turb_intensity_mod = (combined_turb - 0.5) * 2.0 * turbulence_intensity;
float hot_spot = pow(max(0.0, combined_turb - 0.6) * 2.5, 2.0) * turbulence_intensity;
vec3 inner_color = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 0.95);
vec3 temp_color = mix(inner_color, base_color, pow(radial_t, 0.6));
temp_color = mix(temp_color, inner_color, hot_spot * 0.5);
float base_intensity = remap(radial_t, 0.0, 1.0, 1.35, -2.5);
vec3 rotated_pos = rotate_about_axis(planar_disc_pos, disc_dir, 0.01);
float safe_radius = max(radius, 1e-6);
float doppler_dist = (length(rotated_pos - camera_pos) - length(planar_disc_pos - camera_pos)) / safe_radius;
float doppler_contribution = doppler_dist * disc_speed * doppler_beaming_factor * (1.0 - radial_t * 0.7);
float intensity = base_intensity + doppler_contribution + turb_intensity_mod + hot_spot * 1.5;
intensity = clamp(intensity, -3.0, 3.0);
vec3 new_color = hdr_intensity(temp_color, intensity);
vec3 hsv = rgb_to_hsv(new_color);
float hue_shift = clamp(remap(radial_t, hue_radius, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0), 0.0, 1.0);
hue_shift += (combined_turb - 0.5) * turbulence_intensity * 0.1;
hsv.x += hue_shift * hue_shift_factor;
new_color = hsv_to_rgb(hsv);
return new_color;
}
void fragment() {
vec3 ray_origin = CAMERA_POSITION_WORLD;
vec3 ray_dir = normalize(frag_pos_ws - ray_origin);
float sphere_radius = 0.5 * min(min(object_scale.x, object_scale.y), object_scale.z);
vec2 outer_sphere = intersect_sphere(ray_origin, ray_dir, centre, sphere_radius);
bool has_sphere = outer_sphere.x < MAX_FLOAT;
vec3 disc_dir = normalize((MODEL_MATRIX * vec4(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0)).xyz);
vec2 radii = disc_safe_radii();
float disc_radius = sphere_radius * radii.y;
float inner_radius = sphere_radius * radii.x;
float scaled_step = step_size * sphere_radius;
float disc_hit = 0.0;
float black_hole_mask = 0.0;
vec3 sample_pos = vec3(MAX_FLOAT, 0.0, 0.0);
vec3 current_ray_pos = has_sphere ? (ray_origin + ray_dir * outer_sphere.x) : (ray_origin + ray_dir);
vec3 current_ray_dir = ray_dir;
float event_horizon_radius = ss_radius * sphere_radius;
if (has_sphere) {
for (int i = 0; i < ray_steps; i++) {
vec3 dir_to_centre = centre - current_ray_pos;
float dst_to_centre = length(dir_to_centre);
if (dst_to_centre <= event_horizon_radius) {
black_hole_mask = 1.0;
break;
}
dir_to_centre /= dst_to_centre;
if (dst_to_centre > sphere_radius + scaled_step) {
break;
}
vec3 prev_ray_pos = current_ray_pos;
float prev_plane_dist = dot(prev_ray_pos - centre, disc_dir);
float norm_dst = max(dst_to_centre / sphere_radius, 1e-4);
float force = g_const / (norm_dst * norm_dst);
current_ray_dir = normalize(current_ray_dir + dir_to_centre * force * step_size);
current_ray_pos += current_ray_dir * scaled_step;
float curr_dst_to_centre = length(current_ray_pos - centre);
float falloff_zone = event_horizon_radius * 1.5;
if (falloff_zone > event_horizon_radius + 1e-6 && curr_dst_to_centre < falloff_zone) {
float proximity = 1.0 - (curr_dst_to_centre - event_horizon_radius) / (falloff_zone - event_horizon_radius);
black_hole_mask = max(black_hole_mask, clamp(proximity, 0.0, 1.0));
}
if (curr_dst_to_centre <= event_horizon_radius) {
black_hole_mask = 1.0;
break;
}
float curr_plane_dist = dot(current_ray_pos - centre, disc_dir);
if (disc_hit < 1.0 && prev_plane_dist * curr_plane_dist < 0.0) {
float interp = abs(prev_plane_dist) / (abs(prev_plane_dist) + abs(curr_plane_dist));
vec3 crossing_pos = mix(prev_ray_pos, current_ray_pos, interp);
vec3 planar_offset = crossing_pos - centre - dot(crossing_pos - centre, disc_dir) * disc_dir;
float radial_dist_sqr = dot(planar_offset, planar_offset);
float outer_fade_radius = disc_radius * 1.3;
if (radial_dist_sqr < outer_fade_radius * outer_fade_radius) {
disc_hit = 1.0;
sample_pos = crossing_pos;
}
}
if (disc_hit > 0.0 && abs(curr_plane_dist) > abs(prev_plane_dist)) {
break;
}
}
}
vec2 uv = vec2(0.0);
vec3 planar_disc_pos = vec3(0.0);
float streaks = 1.0;
float radial_falloff = 1.0;
if (sample_pos.x < MAX_FLOAT) {
planar_disc_pos = sample_pos - dot(sample_pos - centre, disc_dir) * disc_dir - centre;
uv = disc_uv(planar_disc_pos, disc_radius);
uv.y += TIME * disc_speed * 0.1;
float inner_norm = radii.x / radii.y;
float radius_norm = clamp((uv.x - inner_norm) / max(1.0 - inner_norm, 1e-4), 0.0, 1.0);
streaks = soft_edge(radius_norm, uv.y * PI * 2.0, TIME);
float radial_dist = length(planar_disc_pos) / disc_radius;
radial_falloff = 1.0 - smoothstep(0.85, 1.3, radial_dist);
}
float tex_col = texture(disc_texture, uv).r;
vec2 screen_uv = SCREEN_UV;
vec3 distorted_ray_dir = has_sphere ? current_ray_dir : ray_dir;
vec4 ray_camera_space = VIEW_MATRIX * vec4(distorted_ray_dir, 0.0);
vec4 ray_uv_projection = PROJECTION_MATRIX * vec4(ray_camera_space.xyz, 0.0);
vec2 distorted_screen_uv = ray_uv_projection.xy * 0.5 + 0.5;
float ray_bend = 1.0 - dot(ray_dir, current_ray_dir);
float bend_blend = smoothstep(0.0, 0.15, ray_bend);
float edge_fade_x = smoothstep(0.0, 0.15, min(screen_uv.x, 1.0 - screen_uv.x));
float edge_fade_y = smoothstep(0.0, 0.15, min(screen_uv.y, 1.0 - screen_uv.y));
float lens_blend = has_sphere ? bend_blend * edge_fade_x * edge_fade_y : 0.0;
distorted_screen_uv = mix(screen_uv, distorted_screen_uv, lens_blend);
vec3 background_col = texture(screen_texture, distorted_screen_uv).rgb * (1.0 - black_hole_mask);
vec3 final_disc_col = calc_disc_color(disc_color.rgb, planar_disc_pos, disc_dir, ray_origin, uv.x, uv.y, disc_radius, TIME);
float horizon_fade = 1.0;
if (sample_pos.x < MAX_FLOAT) {
float sample_dist_to_centre = length(sample_pos - centre);
if (event_horizon_radius > 1e-6) {
float fade_center = event_horizon_radius * 1.2;
float fade_width = max(fwidth(sample_dist_to_centre) * 2.0, event_horizon_radius * 0.15);
horizon_fade = smoothstep(fade_center - fade_width, fade_center + fade_width, sample_dist_to_centre);
}
}
disc_hit *= tex_col * disc_color.a * streaks * horizon_fade * radial_falloff;
vec3 col = mix(background_col, final_disc_col, disc_hit);
ALBEDO = col;
ALPHA = 1.0;
}
Further Reading
- Gravitational lensing by spinning black holes - The Interstellar paper
- Shadertoy: Black Hole - Simpler implementations to study
- Inigo Quilez's articles - Essential reading for any shader work